
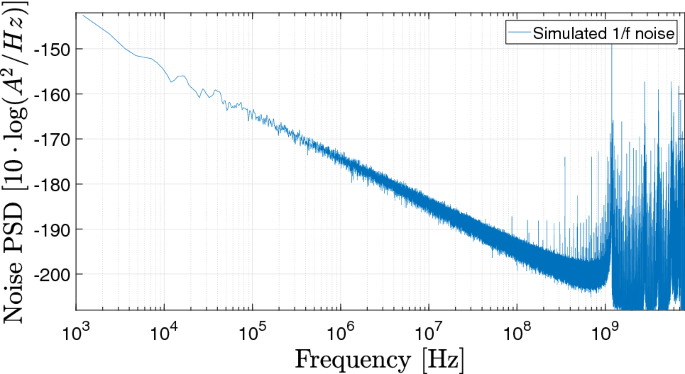
A synchronous detector that samples the peaks of the AC signal, which are equivalent to the original DC value. AC-coupled stages filters out the DC component this also attenuates the flicker noise. Now the signal chain carries an AC, not DC, signal. For example, the signal of interest can be chopped with a frequency. One powerful technique involves moving the signal of interest to a higher frequency and using a phase-sensitive detector to measure it. At very low frequencies, you can think of the noise as becoming drift, although the mechanisms causing drift are usually distinct from flicker noise. Removal in instrumentation and measurements įor DC measurements 1/ f noise can be particularly troublesome, as it is very significant at low frequencies, tending to infinity with integration/averaging at DC. Conventional spectrum analyzers still have better SNR due to their narrow-band acquisition. They reduce the noise by taking multiple sample traces and averaging them. Sampling instruments are broadband, and hence high noise. Unfortunately, these instruments do not operate at frequencies low enough to fully measure flicker noise. Conventional spectrum analyzers that sweep a narrow filtered band over the signal have good signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), since they are narrow-band instruments. Thus the upper and the lower half decades of the obtained power density spectrum are usually discarded from the spectrum. This procedure gives correct spectral data only deeply within the frequency window determined by the reciprocal of the duration of the finite-time sample (low-frequency end) and the digital sampling rate of the noise (high-frequency end). It is then normalized by the duration of the finite-time sample and also by a numerical constant in the order of 1 to get its exact value. The resulting pattern is proportional to the power-density spectrum of the measured noise. Then, after calculating the squared absolute value of the Fourier spectrum, they calculate its average value by repeating this sampling process by a sufficiently large number of times.
Sampling spectrum analyzers take a finite-time sample from the noise and calculate the Fourier transform by FFT algorithm. The measurement of 1/ f noise spectrum in voltage or current is done in the same way as the measurement of other types of noises. ( December 2016) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message) Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Since flicker noise is related to the level of DC, if the current is kept low, thermal noise will be the predominant effect in the resistor, and the type of resistor used may not affect noise levels, depending on the frequency window. In contrast, wire-wound resistors have the least amount of flicker noise. įlicker noise is found in carbon-composition resistors and in thick-film resistors, where it is referred to as excess noise, since it increases the overall noise level above the thermal noise level, which is present in all resistors. This is an empirical model and generally thought to be an oversimplification.
The flicker-noise voltage power in MOSFET is often modeled as K C ox ⋅ W L f is the oxide capacitance in MOSFET devices, W and L are channel width and length respectively. It is generated by a linear mechanism in resistors and FETs, but a non-linear mechanism in BJTs and diodes. It typically has a Gaussian distribution and is time-reversible. MOSFETs have a higher f c (can be in the GHz range) than JFETs or bipolar transistors, which is usually below 2 kHz for the latter.

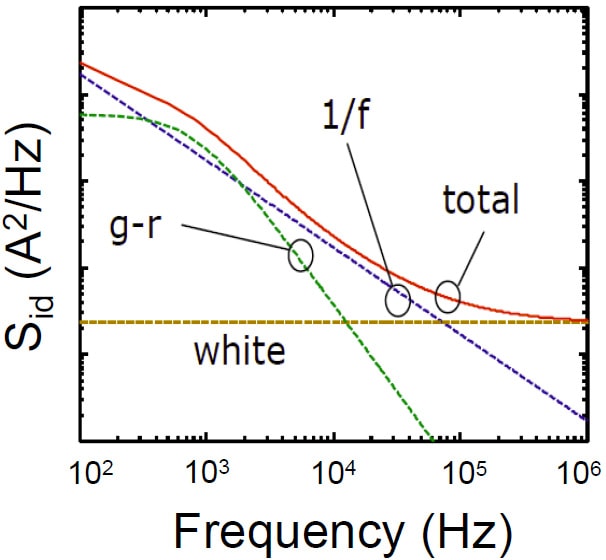
In oscillators, however, the low-frequency noise can be mixed up to frequencies close to the carrier, which results in oscillator phase noise.įlicker noise is often characterized by the corner frequency f c between the region dominated by the low-frequency flicker noise and the higher-frequency "flat-band" noise. In electronic devices, it shows up as a low-frequency phenomenon, as the higher frequencies are overshadowed by white noise from other sources. This effect is not present in manganin, as it has negligible temperature coefficient of resistance. There is also a 1/ f component in resistors with no direct current through them, likely due to temperature fluctuations modulating the resistance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
